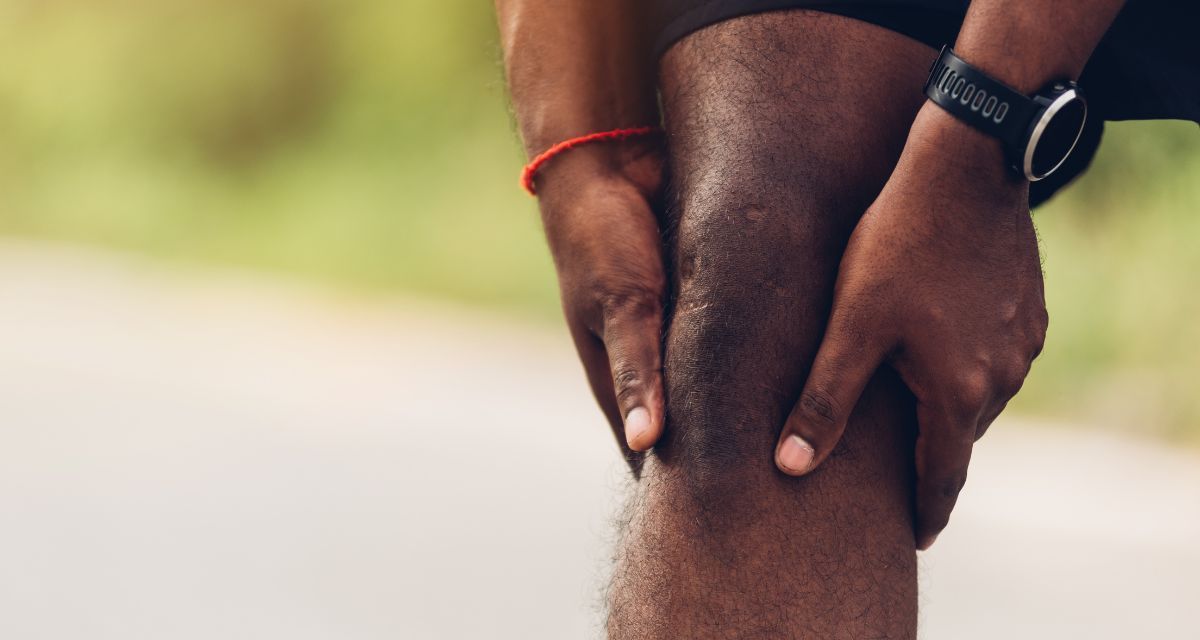
Foot & Ankle Condition We Treat
-
Traumatic Injuries
Button -
Degerative Disorders
Button -
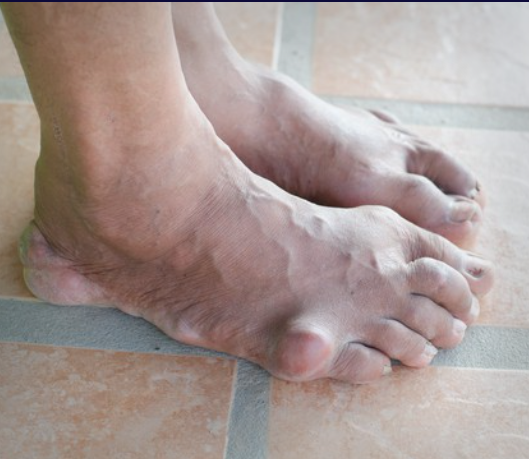
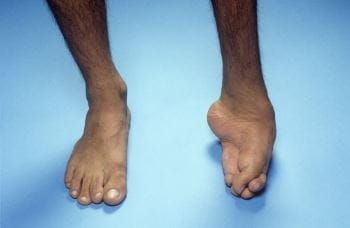
Structural Abnormalities
Button -
Nerve Related Disorders
Button -
Diabetic Foot Disorders
Button -
Skin & Nail Disorders
Button -
Circulatory DIsorders
Button -
Inflammatory Disorders
Button -
Congentital Disorders
Button -
Tumors
Button -
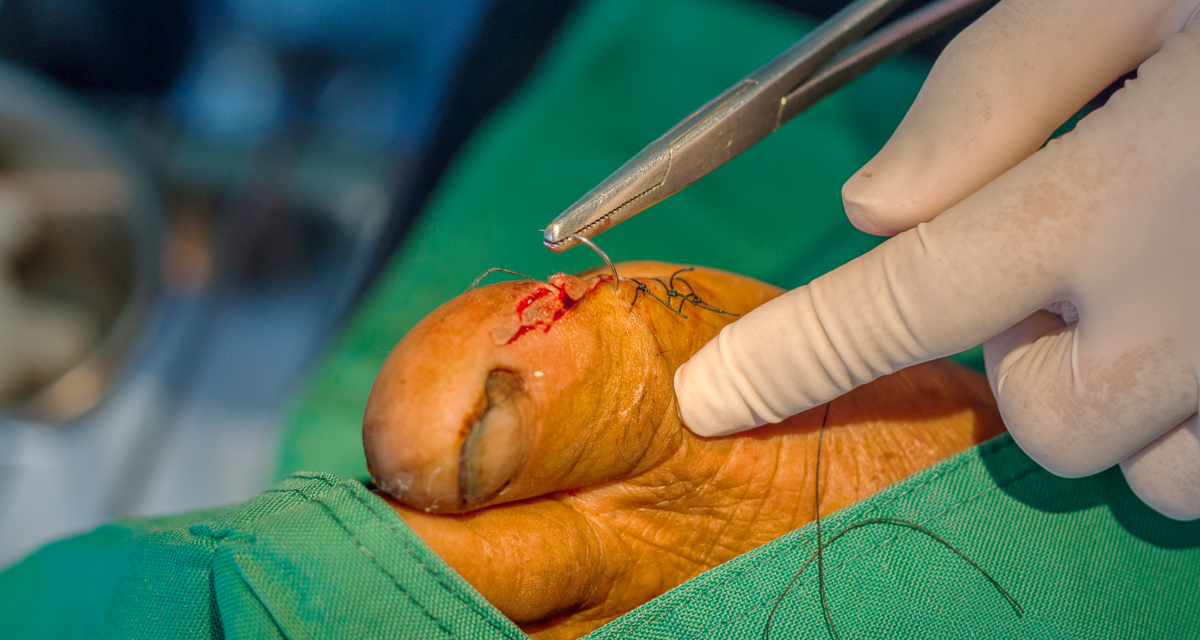
Surgical Management of Foot & Ankle
Button










 Mohammad Khalil" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
Mohammad Khalil" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
 Nsima Usen" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
Nsima Usen" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
 Basil Awawdeh" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
Basil Awawdeh" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
 Ramsha Samra" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>
Ramsha Samra" loading="lazy" class="sc-eqUAAy eTsRji" onerror="handleImageLoadError(this)"/>